Political Background:
A unified Thai kingdom was established in the mid-14th century. Known as Siam until 1939, Thailand is the only Southeast Asian country never to have been taken over by a European power. A bloodless revolution in 1932 led to a constitutional monarchy. In alliance with Japan during World War II, Thailand became a US ally following the conflict.
Climate:
tropical; rainy, warm, cloudy southwest monsoon (mid-May to September); dry, cool northeast monsoon (November to mid-March); southern isthmus always hot and humid
Population:
64,631,595 (As of June, 2006)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 22% (male 7,284,068/female 6,958,632)
15-64 years: 70% (male 22,331,312/female 22,880,588)
65 years and over: 8% (male 2,355,190/female 2,821,805) (2006 est.)
Median age:
male: 31.1 years
female: 32.8 years (2006 est.)
Population growth rate:
0.68% (2006 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.84 male(s)/female
total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2006 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
male: 69.95 years
female: 74.68 years (2006 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
1.5%
Ethnic groups:
Thai 75%, Chinese 14%, other 11%
Religions:
Buddhist 94.6%, Muslim 4.6%, Christian 0.7%, other 0.1% (2000 census)
Government type:
constitutional monarchy
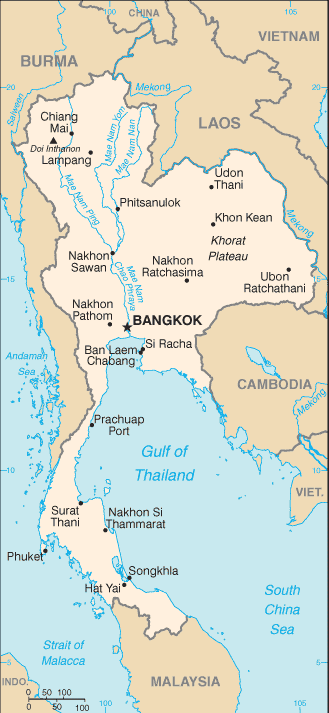
Capital:
Bangkok
Administrative divisions:
76 provinces
Political parties and leaders:
Democrat Party or DP (Prachathipat Party) [ABHISIT Wetchachiwa]; People's Party or PP (Mahachon Party) [ANEK Laothamatas]; Thai Nation Party or TNP (Chat Thai Party) [BARNHARN SILPA-ARCHA]; Thai Rak Thai Party or TRT [THAKSIN Chinnawat]
Economy - overview:
With a well-developed infrastructure, a free-enterprise economy, and pro-investment policies, Thailand appears to have fully recovered from the 1997-98 Asian Financial Crisis. The country was one of East Asia's best performers in 2002-04. Boosted by increased consumption and strong export growth, the Thai economy grew 6.9% in 2003 and 6.1% in 2004 despite a sluggish global economy. Bangkok has pursued preferential trade agreements with a variety of partners in an effort to boost exports and to maintain high growth. In 2004, Thailand and the US began negotiations on a Free Trade Agreement. In late December 2004, a major tsunami took 8,500 lives in Thailand and caused massive destruction of property in the southern provinces of Krabi, Phangnga, and Phuket. Growth slowed to 4.4% in 2005. The downturn can be attributed to high oil prices, weaker demand from Western markets, severe drought in rural regions, tsunami-related declines in tourism, and lower consumer confidence. Moreover, the THAKSIN administration's expansionist economic policies, including plans for multi-billion-dollar mega-projects in infrastructure and social development, has raised concerns about fiscal discipline and the health of financial institutions. On the positive side, the Thai economy performed well beginning in the third quarter of 2005. Export-oriented manufacturing - in particular automobile production - and farm output are driving these gains. In 2006, the economy should benefit from an influx of investment and a revived tourism sector; however, a possible avian flu epidemic could significantly harm economic prospects throughout the region.
GDP (purchasing power parity):
$560.7 billion (2005 est.)
Labor force - by occupation:
agriculture: 49%
industry: 14%
services: 37% (2000 est.)
Unemployment rate:
1.4% (September 2005)
Population below poverty line:
10% (2004 est.)
Industries:
tourism, textiles and garments, agricultural processing, beverages, tobacco, cement, light manufacturing such as jewelry and electric appliances, computers and parts, integrated circuits, furniture, plastics, automobiles and automotive parts; world's second-largest tungsten producer and third-largest tin producer
Currency (code):
baht (THB)
Exchange rates:
baht per US dollar - 40.22 (2005), 40.222 (2004), 41.485 (2003), 42.96 (2002), 44.432 (2001)
Internet country code:
.th
Military branches:
Royal Thai Army, Royal Thai Navy (includes Royal Thai Marine Corps), Royal Thai Air Force
Military service age and obligation:
21 years of age for compulsory military service; males are registered at 18 years of age; conscript service obligation - two years; 18 years of age for voluntary military service (2004)
|